In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud security, identities have become the new perimeter. As organizations migrate to the cloud, the attack surface has shifted from traditional network boundaries to the complex web of user accounts, service accounts, APIs, and permissions that define modern cloud environments. This shift has given rise to a critical discipline: Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM).
IASM is not just another buzzword—it’s a game-changer for cloud security. By focusing on securing identities, IASM helps organizations proactively identify and mitigate risks, reduce their attack surface, and build a resilient security posture.
In this blog, we’ll explore what IASM is, its key features, how it fits into broader cloud security strategies, and why it’s essential for enterprises in 2025.
What is Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM)?
Definition and Core Concepts
Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM) is the practice of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with identities in cloud environments. It focuses on securing user accounts, service accounts, APIs, and permissions to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
At its core, IASM is about visibility and control. It provides organizations with a comprehensive view of their identity landscape, enabling them to detect misconfigurations, over-permissioned accounts, and other vulnerabilities.
Also Read: Understanding and Mitigating Identity Attack Surface in Cloud Environments | 1st of 4
How IASM Differs from Traditional IAM
While traditional Identity and Access Management (IAM) focuses on managing access controls, IASM takes a broader, more proactive approach. Here’s how they differ:
- IAM: Manages who has access to what and enforces policies.
- IASM: Identifies and mitigates risks associated with identities, such as misconfigurations and excessive permissions.
- In short, IAM is about control, while IASM is about risk management.
Also Read: Top 5 Strategies to Minimize Cloud Attack Surface in 2025 | 2nd of 4
Key Features of IASM Tools
Visibility into Identity Risks and Misconfigurations
One of the primary features of IASM tools is their ability to provide real-time visibility into identity risks. These tools scan your cloud environment to identify misconfigurations, over-permissioned accounts, and other vulnerabilities.
For example, an IASM tool might flag a service account with excessive permissions or an API that lacks proper authentication.
Actionable Tip: Use IASM tools to create an inventory of all identities and their permissions. Regularly review this inventory to identify and address risks.

Automated Remediation of Identity Vulnerabilities
IASM tools go beyond detection—they also offer automated remediation. For instance, if an IASM tool identifies an over-permissioned account, it can automatically adjust the permissions or notify the security team for further action.
This automation reduces the burden on security teams and ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed quickly.
Actionable Tip: Look for IASM tools that offer automated remediation features to streamline your security operations.
Integration with Cloud Security Frameworks
IASM tools are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing cloud security frameworks, such as zero-trust architectures and cloud-native security tools. This integration ensures that identity risks are addressed as part of a holistic security strategy.
For example, an IASM tool might integrate with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to provide real-time alerts and insights.
Actionable Tip: Choose IASM tools that integrate with your existing security stack to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
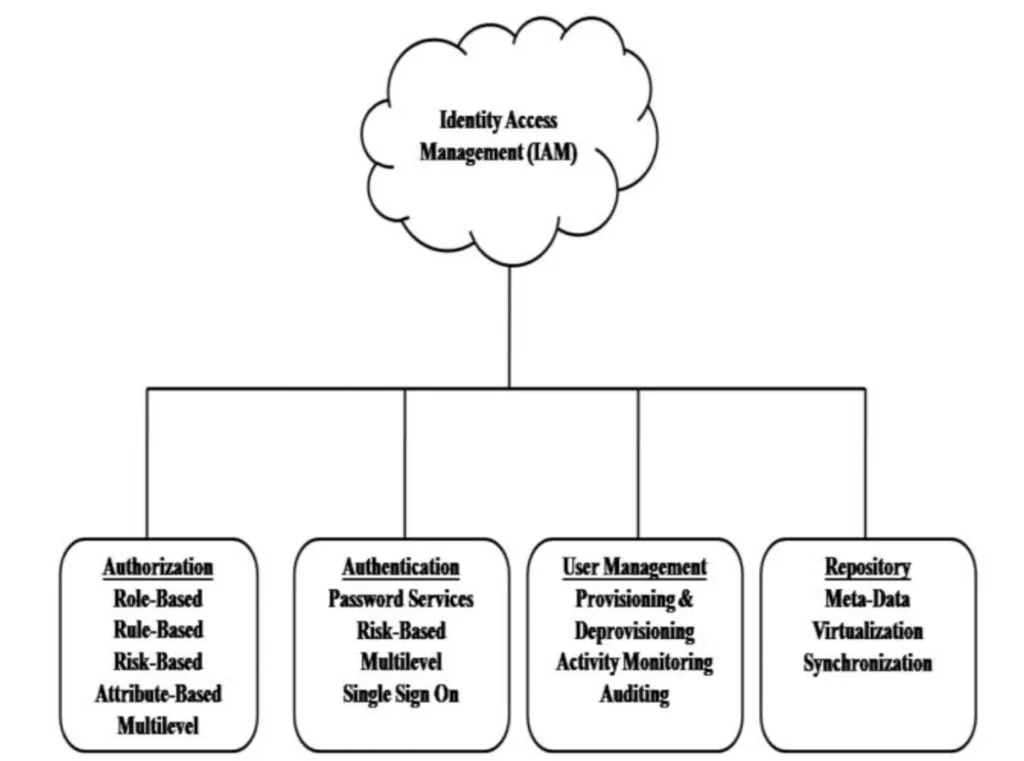
How IASM Fits into Broader Cloud Security Strategies
Complementing Zero-Trust Architectures
Zero-trust is a security model that assumes no user or device is trusted by default. IASM complements zero-trust by providing the visibility and control needed to enforce zero-trust principles.
For example, IASM tools can identify over-permissioned accounts and enforce least privilege access, a key tenet of zero-trust.
Actionable Tip: Use IASM to strengthen your zero-trust strategy by continuously monitoring and securing identities.
Enhancing Cloud-Native Security Tools
Cloud-native security tools, such as AWS IAM, Azure AD, and Google Cloud Security Command Center, are essential for securing cloud environments. However, they often lack the depth and breadth of IASM tools. That’s where Cy5’s ion Cloud Security comes into play, as it provides comprehensive visibility of multi-cloud environment and graph-correlated identity risks.
IASM enhances these tools by providing additional insights and automation capabilities. For instance, while AWS IAM can manage access controls, an IASM tool can identify and remediate identity risks across multiple cloud platforms.
Actionable Tip: Combine IASM tools with cloud-native security tools to create a comprehensive security strategy.

Benefits of Adopting IASM for Enterprises
Proactive Risk Mitigation
IASM enables organizations to take a proactive approach to cloud security. By identifying and addressing identity risks before they are exploited, IASM helps prevent breaches and minimize damage.
For example, an IASM tool might detect a misconfigured API and remediate it before attackers can exploit it.
Improved Compliance and Governance
Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA requires organizations to maintain strict control over access to sensitive data. IASM helps organizations meet these requirements by providing visibility into identity risks and enforcing access controls.
Actionable Tip: Use IASM tools to generate compliance reports and demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
Reducing the Likelihood of Identity-Based Breaches
Identity-based breaches, such as credential theft and privilege escalation, are among the most common types of cloud breaches. By securing identities, IASM significantly reduces the likelihood of these breaches.
For example, an IASM tool might detect and remediate an over-permissioned service account, preventing attackers from using it to escalate privileges.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing IASM
Overcoming Tool Sprawl and Integration Issues
One of the challenges of implementing IASM is tool sprawl. Organizations often use multiple security tools, each with its own interface and workflow. Integrating IASM tools with these existing tools can be complex and time-consuming.
Actionable Tip: Choose IASM tools that offer robust integration capabilities and work with your existing security stack.
Ensuring Scalability in Large Cloud Environments
As organizations grow, their cloud environments become more complex. Ensuring that IASM tools can scale to meet the needs of large, dynamic environments is critical.
Actionable Tip: Test IASM tools in a pilot environment before rolling them out organization-wide. Ensure they can handle the scale and complexity of your cloud environment.
Conclusion: The Future of IASM in Cloud Security
The Growing Importance of Identity-Centric Security
As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, identity-centric security will become increasingly important. IASM is at the forefront of this shift, providing organizations with the tools and insights needed to secure their identities and reduce their attack surface.
Predictions for IASM Adoption and Innovation
In the coming years, we can expect to see widespread adoption of IASM as organizations recognize its value. We’ll also see continued innovation in IASM tools, with advancements in AI, automation, and integration capabilities.
By adopting IASM today, organizations can stay ahead of emerging threats and build a secure, resilient cloud environment.
Final Thoughts
Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM) is not just a trend—it’s a necessity for modern cloud security. By focusing on securing identities, IASM helps organizations proactively mitigate risks, improve compliance, and reduce the likelihood of breaches.
As you navigate the complexities of cloud security, remember that identities are the new perimeter. Don’t leave them unprotected.
Check Out More Research and Insights from Cy5
-
Decoding the tj-actions/changed-files Supply Chain Attack | Part 1/3
-
Cloud Security Architecture: Building a Resilient Infrastructure
FAQs: Identity Attack Surface Management
Identity Attack Surface Management (IASM) is a security practice focused on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with identities in cloud environments. It addresses vulnerabilities like over-permissioned accounts, misconfigured APIs, and unsecured service accounts. IASM provides visibility into identity sprawl and automates remediation to prevent breaches. With 90% of breaches involving identity-related exploits, IASM is critical for reducing attack vectors in cloud ecosystems.
Traditional IAM focuses on authentication and access control, while IASM takes a proactive risk management approach. IAM enforces “who has access to what,” whereas IASM identifies risks like excessive permissions, dormant accounts, and misconfigurations. For example, IASM tools map privilege escalation paths and enforce least privilege, whereas IAM tools might only manage role assignments.
Top features include:
1. Continuous Identity Discovery: Inventory human and non-human identities (e.g., API keys, service accounts) across hybrid environments.
2. Automated Remediation: Fix misconfigurations (e.g., revoke unused permissions) without manual intervention.
3. Integration with SIEM/XDR: Correlate identity risks with broader threat detection systems.
4. Risk Prioritization: Highlight high-impact vulnerabilities like admin accounts with stale credentials.
Zero Trust mandates “never trust, always verify,” and IASM operationalizes this by enforcing least privilege access and continuous monitoring. For instance, IASM tools detect and remediate overprivileged accounts, ensuring users only retain necessary access. This aligns with Zero Trust principles like micro-segmentation and real-time risk assessment.
Proactive Risk Mitigation: Identify and remediate vulnerabilities before exploitation (e.g., exposed service account keys).
Compliance Assurance: Automate audits for regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by documenting access controls.
Reduced Breach Likelihood: Address 93% of preventable identity-related breaches through automated controls.
Tool Sprawl: Integrating IASM with legacy IAM, PAM, and cloud-native tools can create complexity.
Scalability Issues: Managing identities in large, multi-cloud environments requires tools that handle dynamic scaling.
Human Error: Over 75% of breaches involve human factors like misconfigurations, necessitating employee training.
IASM provides auditable trails of access changes, automates privilege reviews, and enforces least privilege. For example, it flags accounts with unnecessary access to sensitive data, ensuring compliance with GDPR’s “data minimization” principle. Automated reports simplify audits and demonstrate adherence to regulatory frameworks.
AI-Driven Automation: Machine learning will predict risks (e.g., anomalous login patterns) and auto-remediate issues.
Password-less Authentication: Biometrics and FIDO2 keys will reduce reliance on vulnerable credentials.
Unified Identity Ecosystems: Convergence of IAM, PAM, and IGA tools under IASM platforms for holistic visibility.





