As India continues to rise high on technological advancement with digitization takin over businesses operations more than ever. The recently published guidelines by CERT-In (effective from 25th of July 2025), quite appropriately attributes to the overall expectation of public cloud services market to grow at CAGR of 24.3% for 2023-28. In fact, cloud adoption in India has surged by 54% in 2024 alone (Source: Statista). These new guidelines defines a complete cyber security audit (Version 1.0, 25.07.2025) to be carried out to redefine how organizations/businesses must secure their digital operations. In this blog, we will be covering the aspects of cloud security being covered within the guidelines under the purview of security audit. The guidelines places special emphasis on securing cloud environments Non-compliance now risks operational suspension or debarment from government contracts (Section 19). For the organizations who are heavily reliant on public clouds, the rules redefine risk management to prioritize proactive controls over reactive fixes.
Core Cloud Security Requirements in 2025 CERT-In Guidelines
The latest cyber security audit guidelines released by CERT-In re-emphasizes on five pivotal mandates for cloud environments. The are the following-
1. Annual Cloud Security Testing
Where you can find? Page 16. Section 6. Point xviii
Evaluation and assessment of security configurations, measures, and vulnerabilities of cloud-based environments, applications, and infrastructures.
2. 180-Days Log Retention
Where you can find? Page 17. Section 6. Point xxi. Log Management and Maintenance Audit
Carrying out assessments to evaluate the completeness and effectiveness of cloud-based systems by generation, retaining, and monitoring of logs. This evaluation should be done as per the organizational policies, which in turn should be incorporated by aligning with regulatory requirements to ensure detection, investigation, and response.
3. CSA CCM Framework Adoption
Where you can find? Page 22. Section 8. Point ii. CSA Cloud Control Matrix
CSA CCM is a cloud security standard that consists of 197 control objects across 17 domains, which helps in assessment and guidance for implementation. This framework is formidable to adapt different cloud service models.
4. Least Privilege Enforcement
Where you can find? Page 28. Section 9.6. Point iv. Asset Management and Infrastructure Security
The organizations should enforce the practice of least privilege across certain cyber assets, which translates to minimum level of access given to systems, users, processes, and applications. This ensures that only necessary access is provided to perform specific role and function. It is one of the prominent security control to prevent exploitation and security breach.
5. Vendor Risk Assessments
Where you can find? Page 17. Section 6. Point xxiv. Asset Management and Infrastructure Security
The organizations must carry out assessment of cybersecurity practices for vendors and third-party to identify and prevent supply chain risks and ensure enforcement of security policies.
Also Read: Cloud Security Best Practices for 2025
Alignment of Cloud Security Audit with the Help of Cy5’s Ion
Cy5’s ion cloud security platforms comes with modules and components that helps organizations to achieve compliance in accordance to these new guidelines for carrying out cloud security audit under the purview of cyber security audit policy.
| Cloud Tool | Section in CERT-In New Guideline Policy Document | Key Compliance Function |
| CSPM | 8.ii, 6.xviii | Continuous misconfiguration monitoring via CSA CCM |
| KSPM | 6.xviii, 9.6.iii | Container/Kubernetes policy enforcement |
| SIEM | 6.xxi, 5 | 180-day log retention for incident analysis |
| CIEM | 9.6.iv, 6.xxiv | Identity governance & third-party access control |
Essential Compliance Insight
CERT-In mandates CSA CCM as the baseline for cloud configurations (Section 8.ii). CSPM tools automate this alignment, scanning for deviations like exposed storage buckets or non-compliant network rules—key for annual audit evidence (6.xviii).
Cy5’s Cloud Security Tools Mapped to CERT-In Requirements
Following are the list of modules/components available in Cy5’s ion Cloud Security platform that helps leading organizations like Physics Wallah, Bharti Airtel, IND Money, Zupee, Hero Vired, Eureka Forbes, etc., to secure their multi-cloud environments. These modules will not only help in security your cloud infrastructure but will also help the organizations in getting CERT-in compliant as per these new cyber security audit guidelines.
CSPM: Your Cloud Configuration Firewall
CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) continuously validates settings against CSA CCM benchmarks (Section 8.ii). It detects high-risk misconfigurations—unencrypted databases, overly permissive S3 buckets—mandated for remediation under Section 6.xviii. For audits, CSPM generates automated reports proving infrastructure compliance.
Must Read: CSPM Explained: Boost Cloud Security with Posture Management
KSPM: Kubernetes Hardening Made Auditable
KSPM (Kubernetes Security Posture Management) enforces secure container configurations (Section 9.6.iii) and runtime policies. Per Section 6.xviii, organizations must audit cluster settings (RBAC, pod security) quarterly. KSPM automates checks for CVSS-scored vulnerabilities (5.xxiv), ensuring production environments resist compromises.
SIEM: The 180-Day Logging Imperative
SIEM solutions aren’t optional—Section 6.xxi requires centralized logging with 180-day retention for cloud workloads. This supports forensic investigations (Section 5) and real-time threat detection. Logs must include access events, network flows, and API calls, with integrity hashing to prevent tampering.
CIEM: Slashing Overprivileged Access
CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management) operationalizes least privilege (Section 9.6.iv). By automating entitlement reviews, it eliminates excessive permissions for employees and vendors—a key focus area during third-party risk audits (6.xxiv). CIEM also maps access paths to critical assets, simplifying compliance proofs.
VM/CDR: Closing the Detection-Response Loop
-
Vulnerability Management (VM): Scans cloud workloads using CERT-In’s required CVSS/EPSS scoring (Section 5.xxiv), prioritizing patch cycles.
-
Cloud Detection & Response (CDR): Provides runtime threat hunting aligned with production environment security (5.xv) and incident response mandates (6.xviii).
Why Least Privilege Isn’t Optional:
Section 9.6.iv explicitly requires identity minimization across cloud environments. CIEM tools automate this by revoking stale permissions and enforcing Just-in-Time access—critical for limiting breach impact during vendor audits (6.xxiv).
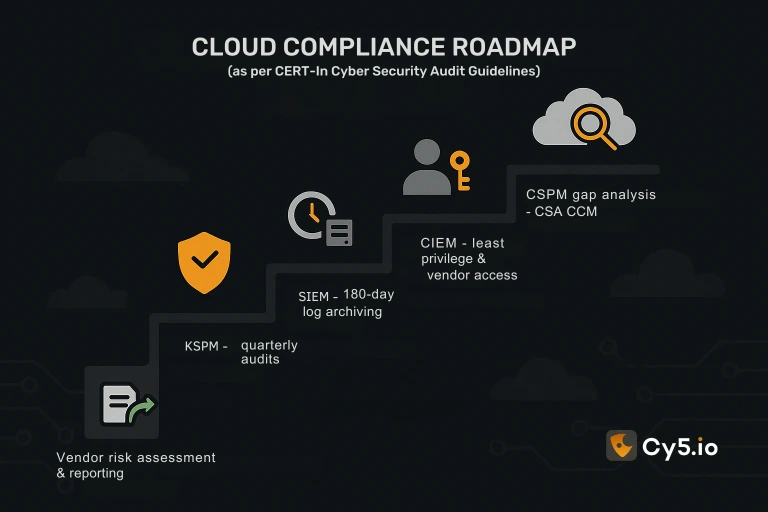
5-Step CERT-In Cloud Compliance Roadmap
Based on the guidelines, prioritize these actions:
-
Conduct CSPM gap analysis: Map current cloud configurations against CSA CCM (Section 8.ii).
-
Deploy CIEM: Audit identities and enforce least privilege (9.6.iv), especially for third parties.
-
Configure SIEM retention: Validate 180-day logging (6.xxi) with WORM storage.
-
Schedule KSPM scans: Quarterly container audits per Section 6.xviii.
-
Document vendor risks: Assess CSP shared responsibility alignment (6.xxiv).
Penalty Avoidance Checklist
Non-compliance penalties (Section 19) include service suspension. To mitigate risk:
- Retain vulnerability scan reports for 3 years
- Encrypt all audit trails
- Formalize cloud testing schedules annually
Conclusion: Compliance as Competitive Advantage
CERT-In’s 2025 guidelines transform cloud security from an optional layer to an operational imperative. With non-compliance risking debarment (Section 19), proactive adoption of CSPM, KSPM, and CIEM isn’t just regulatory—it’s strategic resilience. Employ Cy5’s ion Cloud Security platform in your cloud infrastructure and become compliant along with sustaining the reputation and trust of securing your data.
“CERT-In cloud compliance requirements mandate 180-day SIEM logging (Section 6.xxi), CSA CCM-aligned CSPM configurations (8.ii), and least privilege enforcement via CIEM (9.6.iv). Non-compliance risks operational suspension.”
FAQs: New CERT-In Guidelines (2025)
The new CERT-In 2025 guidelines emphasize five mandatory priorities: annual cloud security testing, centralized 180-day log retention, least-privilege enforcement, vendor risk assessment, and continuous compliance mapping using frameworks like CSA CCM.
These priorities focus on ensuring accountability and traceability within India’s rapidly expanding cloud ecosystem. Organizations must demonstrate that they can detect, log, and report incidents within mandated timeframes. CERT-In expects proactive security testing of configurations, workloads, and access policies to close gaps before exploitation. Identity management is another focus area — all users and systems must operate under the principle of least privilege, verified periodically. Companies are also required to maintain visibility into third-party providers and ensure their compliance aligns with India’s security baselines.
This requirement is India-exclusive, applicable to all cloud providers, data centers, intermediaries, and corporate entities under CERT-In’s jurisdiction.
Yes. CERT-In mandates that all covered entities report specific types of cyber incidents within six hours of detection or awareness through the prescribed online form or email.
This 6-hour window is one of the strictest globally and underscores India’s commitment to rapid cyber threat containment. Incidents include unauthorized access, data breaches, identity leaks, or system compromises. Organizations must maintain 24×7 contact points and escalation processes to ensure immediate notification. CERT-In may also request supporting forensic data, including logs and configuration snapshots, to aid national-level incident investigations. Non-compliance may lead to penalties or loss of operating authorization under the IT Act.
This reporting timeline applies across cloud service providers, SaaS platforms, and body corporates operating in India or servicing Indian customers.
All organizations must retain ICT system logs for a minimum of 180 days and provide them to CERT-In when requested.
Logs must cover authentication events, administrative actions, network activity, and API access — across cloud, hybrid, and on-prem workloads. These logs should be stored securely using WORM (Write Once Read Many) or immutable storage to maintain evidentiary integrity. It’s best practice to centralize all logs in a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for quick retrieval and analysis. CERT-In encourages organizations to test their retrieval capability periodically and maintain searchable archives for incident correlation.
This 180-day retention policy is part of Section 6(iv) of CERT-In Directions 2025 and is mandatory for Indian entities and cloud providers.
CERT-In aligns closely with the Cloud Security Alliance’s Cloud Controls Matrix (CSA CCM) and the Indian IT Act Section 70B for baseline cloud controls.
The CSA CCM framework defines 197 controls across 17 domains, including identity, logging, and configuration management — all referenced implicitly by CERT-In for audit readiness. Indian organizations can use CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) tools to automatically map their controls to CCM categories, generate evidence reports, and close non-compliant gaps. This mapping simplifies annual security testing and aligns posture management with the CERT-In 2025 checklist.
CERT-In recognizes CSA CCM and MeitY’s empaneled standards as acceptable references for proving cloud compliance in India.
CERT-In mandates enforcing the principle of least privilege (PoLP) across all users, roles, and service accounts in cloud environments.
Organizations should implement Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) tools to continuously identify and revoke excessive permissions. Admin and service identities must have only the access required for their operational role. Periodic access reviews and “Just-in-Time (JIT)” provisioning help ensure users do not retain stale or toxic permission combinations. CERT-In also recommends MFA for all privileged accounts and quarterly reporting of revoked access to auditors.
This control is enforced under Section 9.6(iv) of CERT-In Directions 2025 and applies to all cloud operators and body corporates in India.
Non-compliance may result in service suspension, financial penalties, and legal proceedings under the Information Technology Act, 2000.
CERT-In has enforcement powers to suspend service authorizations, restrict access to national infrastructure, and blacklist service providers that fail to adhere to directives. Repeat offenders risk being barred from handling sensitive or government data. Fines may be levied for failing to retain logs, not reporting incidents on time, or ignoring audit recommendations. Maintaining audit trails, compliance reports, and documented risk management plans helps avoid enforcement actions.
These penalties are applicable across Indian data centers, intermediaries, cloud platforms, and service providers.
A five-step roadmap helps organizations meet 2025 standards: CSPM gap analysis, CIEM implementation, SIEM-based log retention, quarterly KSPM audits, and vendor risk documentation.
Step 1: Use CSPM tools to align configurations with CSA CCM controls.
Step 2: Deploy CIEM for access governance.
Step 3: Implement SIEM with 180-day retention.
Step 4: Automate Kubernetes and IaC security checks (KSPM).
Step 5: Maintain an evidence pack for vendor assessments and third-party security posture.
CERT-In encourages annual testing of all these controls and maintaining digital artifacts for review.
Applicable to Indian enterprises and cloud-native startups under CERT-In’s jurisdiction.
Yes. CERT-In explicitly includes Kubernetes and containerized workloads within its 2025 compliance directives.
Organizations must adopt Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM) to enforce RBAC controls, network policies, and vulnerability scanning of images. CERT-In recommends quarterly audits of cluster configurations, ensuring only signed, verified images are deployed. Runtime protection and container activity monitoring further demonstrate compliance. Using CNAPPs that integrate KSPM with CSPM provides a unified view for auditors.
This applies to Indian cloud service providers and enterprise DevOps teams using Kubernetes clusters.
CERT-In requires organizations to conduct formal vendor risk assessments and ensure third-party compliance with its cloud directives.
This includes evaluating service-level agreements for log retention, incident reporting, and access management. Vendors must provide evidence of 180-day log retention, least-privilege enforcement, and annual testing. CERT-In expects contractual clauses that bind third parties to share evidence of compliance. Failure to monitor vendor security may make the primary organization liable for breaches.
Vendor oversight is mandated under Section 6(xxiv) of CERT-In Directions and applies to cloud resellers, SaaS vendors, and managed service providers in India.
Organizations must maintain logs, vulnerability scans, annual test reports, and access review documentation for at least three years.
Evidence should include 180-day log archives, records of incident reports (with timestamps), results of annual security assessments, and proof of corrective actions. Access management artifacts (revoked permissions, MFA enforcement) are also reviewed during audits. CERT-In allows digital submission of reports if they’re digitally signed and time-stamped to ensure authenticity.
This evidence applies to Indian cloud operators, intermediaries, and any organization offering digital services.
Annual tests must assess cloud configurations, vulnerabilities, identity policies, and incident response readiness.
CERT-In expects penetration testing and red teaming to validate exposure. Security teams should simulate misconfigurations, weak IAM policies, and API exposures. The final report should detail exploited paths, remediation timelines, and proof of fix. Using CNAPPs helps automate these assessments and correlate them with the 2025 checklist.
Mandatory under Section 6(xviii) for all cloud and digital service providers operating in India.
A compliant SIEM must centralize all ICT logs and store them securely for at least 180 days, ensuring real-time correlation and integrity.
It should ingest events from cloud services, firewalls, identity systems, and endpoints. CERT-In recommends regular integrity checks and time synchronization (via NTP) to preserve forensic accuracy. Alerts should integrate with incident response workflows, ensuring that potential breaches trigger 6-hour reporting. Immutable storage or WORM tiers guarantee log reliability.
This applies to Indian entities and cloud providers subject to CERT-In logging mandates.
Preparation involves aligning internal policies, performing gap analysis, and generating compliance evidence before auditor engagement.
Organizations should create a compliance matrix mapping CERT-In requirements to implemented controls. Conduct mock audits, ensure all log retrievals are validated, and maintain updated policies for incident response and access control. Documentation must include audit reports, policy references, and system diagrams showing secure cloud configurations.
Applies to all Indian enterprises and data-handling organizations audited under the CERT-In framework.
Yes. CERT-In mandates time synchronization of all systems with an approved NTP server to ensure log integrity and correlation.
Accurate timestamps help investigators reconstruct timelines during incidents. Organizations must verify clock drift and ensure that both on-prem and cloud instances sync periodically. Time discrepancies may invalidate log data during audits, so automation of clock synchronization across infrastructure is recommended.
This control applies to Indian cloud and IT infrastructure under CERT-In’s directives.
CERT-In 2025 requires continuous monitoring, 180-day logs, identity governance, vendor accountability, and annual security testing.
Cloud providers must maintain compliance-ready documentation, strengthen IAM practices, and deploy automated CSPM and CIEM solutions. Annual reporting and retention practices are mandatory, and proactive vulnerability management is strongly encouraged. Indian providers that align with these standards can demonstrate audit readiness and win government and enterprise trust.
This applies to Indian cloud service providers and digital infrastructure organizations under the CERT-In mandate.





