In today’s digital-first world, cloud computing has become the backbone of modern businesses. However, as organizations migrate to the cloud, ensuring robust and secure cloud architecture is critical to protect sensitive data, maintain compliance, and mitigate risks. This blog dives deep into the key principles and best practices for designing a secure cloud architecture, helping you build a resilient and future-proof cloud environment.
What is Cloud Security Architecture?
Cloud security architecture refers to the framework and design principles used to secure cloud-based systems, applications, and data. It encompasses a combination of tools, policies, and technologies that work together to protect cloud environments from threats, vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access.
A well-designed secure cloud architecture ensures:
- Data protection: Safeguarding sensitive information from breaches and leaks.
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
- Resilience: Minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Scalability: Adapting to growing business needs without compromising security.
Read More: Cloud Security Architecture: Building a Resilient Infrastructure
Why is Secure Cloud Architecture Important?
With the rise of cyberattacks and data breaches, cloud security architecture is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. According to a recent report, 39% of businesses experienced a data breach in their cloud environment in 2023. A secure cloud architecture helps:
- Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Reduce the risk of costly data breaches.
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations.
- Build trust with customers and stakeholders.
Key Principles of Secure Cloud Architecture
Designing a secure cloud architecture requires adherence to fundamental principles. Here are the key principles to guide your cloud security strategy:
- Defense in Depth
Implement multiple layers of security controls to protect your cloud environment. This includes:
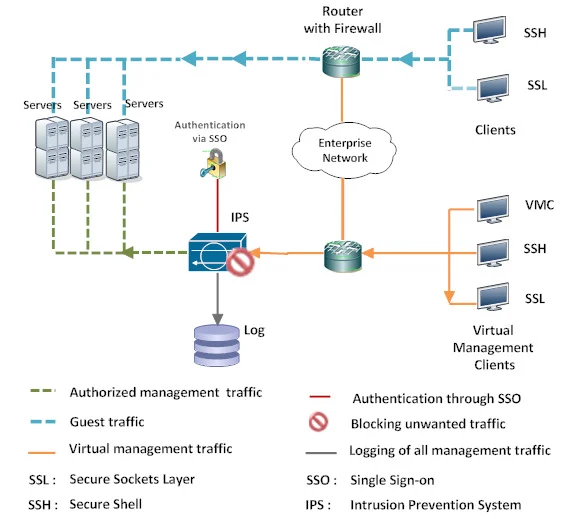
- Network security: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Data encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- Access controls: Role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Least Privilege
Grant users and systems the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and limits the impact of potential breaches.
- Zero Trust Architecture
Adopt a Zero Trust approach, where no user or device is trusted by default, even if they are inside the network. Continuously verify identities and enforce strict access controls.
- Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Implement real-time monitoring and logging to detect and respond to threats promptly. Use tools like **Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)** to identify misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
- Data Encryption
Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Use strong encryption algorithms and manage encryption keys securely.
- Automation and Orchestration
Leverage automation to enforce security policies, patch vulnerabilities, and respond to incidents. Automation reduces human error and ensures consistent security across your cloud environment.
Best Practices for Designing a Secure Cloud Architecture
To build a secure cloud architecture, follow these best practices:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before designing your cloud architecture, identify potential risks and vulnerabilities. Assess your organization’s security requirements and compliance obligations.
- Choose the Right Cloud Service Model
Select a cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS) that aligns with your security needs. Understand the shared responsibility model to determine which security tasks are handled by the provider and which are your responsibility.
- Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Use IAM solutions to manage user identities and permissions. Enforce strong password policies, MFA, and RBAC to control access to cloud resources.
- Secure Your Network
-
- Use firewalls and VPNs to protect your network perimeter.
- Segment your network to limit the spread of threats.
- Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keep your cloud infrastructure and applications up to date with the latest security patches. Vulnerabilities in outdated software are a common entry point for attackers.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery
Implement regular backups and a disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in case of a breach or outage.
- Leverage Cloud Security Tools
Use tools like CSPM, **Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB)**, and **Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)** to enhance your cloud security posture.
- Train Your Team
Educate your employees about cloud security best practices and the importance of following security protocols. Human error is a leading cause of data breaches.
Examples of Secure Cloud Architecture
Here are some real-world examples of secure cloud architecture:
- AWS Cloud Security Architecture
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access.
- Enable AWS CloudTrail for logging and monitoring.
- Implement AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for encryption.
- Azure Cloud Security Architecture
- Use Azure Active Directory (AD) for identity management.
- Enable Azure Security Center for threat detection and response.
- Implement Azure Information Protection for data encryption.
- Google Cloud Security Architecture
- Use Google Cloud IAM for access control.
- Enable Google Cloud Security Command Center for monitoring.
- Implement Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) for encryption.
Conclusion
Designing a secure cloud architecture is essential for protecting your organization’s data and ensuring compliance in today’s threat landscape. By following the key principles and best practices outlined in this blog, you can build a resilient and secure cloud environment that meets your business needs.
Whether you’re a beginner or an enterprise, understanding cloud security architecture is the first step toward safeguarding your cloud infrastructure. Start implementing these strategies today to stay ahead of cyber threats and build trust with your customers.
FAQ: Designing a Cloud Security Architecture
Cloud security architecture is a structured framework of policies, tools, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments. It addresses unique challenges like shared responsibility models, dynamic scalability, and evolving cyber threats. Its importance lies in ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad) of resources, mitigating risks like data breaches, ransomware, and compliance violations. For businesses, it’s essential for maintaining customer trust, avoiding financial penalties, and enabling secure digital transformation.
The shared responsibility model divides security duties between cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure) and customers:
–> Providers secure the underlying infrastructure (e.g., physical servers, hypervisors).
–> Customers protect their data, applications, and access controls.
Responsibilities vary by service model:
1. IaaS: Customers manage OS, apps, and data security.
2. PaaS: Providers handle infrastructure; customers secure apps and configurations.
3. SaaS: Providers manage most security; customers control access and data usage.
Misunderstanding this model is a leading cause of security gaps.
1. Adopt Zero Trust: Enforce least-privilege access and continuous authentication.
2. Automate Security: Use tools like CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) for real-time threat detection and compliance monitoring.
3. Multi-Layered Defense: Combine network security (firewalls), data encryption, IAM, and AI-driven anomaly detection.
4. Regular Assessments: Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scans to identify misconfigurations.
5. Shift-Left Security: Embed security into DevOps pipelines (e.g., IoC scanning).
Compliance requires aligning with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 through:
1. Automated Monitoring: Tools like Cy5’s SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) track policy adherence.
2. Audit Trails: Maintain logs for transparency during regulatory reviews.
3. Policy-as-Code (PaC): Enforce rules programmatically to reduce human error.
4. Vendor Risk Management: Evaluate third-party providers’ compliance certifications.
Non-compliance risks fines and reputational damage, making these steps non-negotiable.
Key technologies include:
1. IAM: Manage user access.
2. CSPM: Automate misconfiguration detection.
3. Encryption: Protect data at rest/in transit (AES-256, TLS).
4. SIEM: Centralize threat monitoring.
5. CASB: Secure SaaS applications and shadow IT.
These tools can be found in prominent leading cloud security platform address top risks like insecure APIs and insider threats while enabling scalability
Run a risk assessment to map assets, threats, compliance requirements, and shared-responsibility gaps before selecting services and controls.
Cloud providers secure the underlying infrastructure; you secure configurations, identities, apps, and data — responsibilities shift by IaaS/PaaS/SaaS.
Defense-in-depth, least privilege/RBAC, Zero Trust verification, continuous monitoring/logging, strong encryption, and automation/orchestration.
Adopt Zero Trust, automate with CSPM, layer defenses (network, IAM, encryption, detection), run regular security assessments, and shift-left in CI/CD.
Use cloud IAM for least privilege + MFA, continuous identity verification, network micro-segmentation, and policy-as-code for enforcement across providers.
CSPM for misconfigurations/compliance drift, SIEM for centralized telemetry, KMS for keys, and CASB for SaaS and shadow IT control.
Automate monitoring, keep audit trails, apply policy-as-code, and validate vendor certifications as part of your governance program.
Standardize IAM and baseline policies across clouds, automate config checks with CSPM, and segment networks to contain lateral movement.
Continuously for configs and logging; plus scheduled pen tests and vulnerability scans each release cycle or at least quarterly.